Cocaine
Cocaine is a narcotic that is usually paired with alcohol for the dual effect. When ingested orally, the effects of cocaine can begin within a few minutes and last up to half an hour.
Cocaine suppresses the reuptake of the hormone norepinephrine, a chemical messenger that sends signals throughout the body. Chronic cocaine users can experience other complications such as chronic red eyes, lesions, and ulcers.
Methamphetamines
Methamphetamines affect the dopamine receptors in the body, which hijacks the reward centerpiece of the brain by increasing production. Thus, methamphetamine users often have a larger-than-life sense of euphoria. The common symptoms of methamphetamine use are dilated pupils, anxiety, and aggression.
LSD and Psilocybin (Mushrooms)
Hallucinogens such as LSD, mescaline, and psilocybin/magic mushrooms can produce symptoms that include restlessness, sleep deprivation, and dilated pupils, also called shroom eyes or mushroom pupils.
Mushrooms can also make your eyes red or bloodshot. The effects of these drugs can range from 6 hours to 12 hours depending on the intake. In popular culture, people often associate dilated pupils with the experience of ingesting one of these substances.
Opiates
According to the CDC, nearly 500,000 people died from overdoses involving opioids, including prescription and illicit opioids, from 1999-2019. Opiates have a series of variations, either used for medical purposes or for illicit means. Due to the stimulation of the opioid receptors, these substances decrease the velocity of pupil dilation when eyes are in contact with light.
The dilated pupil effect that opioids cause usually begins within 15 minutes of use and typically lasts for about one to three hours.
These variations of these substances could be morphine (natural), heroin (semi-synthetic), meperidine and methadone (synthetic), prescription opioids such as hydrocodone, oxycodone, pentazocine, or fentanyl.
MDMA
MDMA (methylenedioxymethamphetamine) is a drug that causes side effects such as pupil dilation, dry mouth, decreased appetite, and increased heart rate. If taken orally, the drug spreads through the bloodstream quickly. The users of this drug often describe feelings of great confidence, insightfulness, heightened senses, and communication.
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are short but fast-acting barbiturates that can be used to offset the side effects of withdrawal. In addition, benzodiazepines are often used with alcohol or other substances for their calming effects. Using benzos for their calming effects can make them lethal though.
Blurred vision and dilated pupils are common visual side effects of benzo use. These symptoms can also be signs of benzo overdose. Other possible symptoms of benzo overdose include decreased heart rate, drowsiness, slurred speech, and coma. Common withdrawl symptoms include “benzo belly“, which includes symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, and appetite changes
In addition, there are several prescribed drugs that cause dilated pupils:
- Antihistamines, such as Benadryl or Unisom
- Antiseizure drugs, Topamax for example
- Decongestants, like Sudafed
- Medication for Parkinson’s disease, such as Symmetrel or Sinemet
- Medicine for heart or stomach conditions, Atropine for exampl
Does Weed (Marijuana/Cannabis) make your pupils big?
Contrary to popular belief, weed does not commonly cause large, dialted pupils. In fact, cannabis use tends to cause minor pupil constriction (miosis) or no significant change in overall size.
The “stoned eye” or “marijuanna pupils” look commonly associated with pot use is most oftenn cause my a combination of:
- Red, bloodshot eyes caused by a lowering blood pressure and dilating blood vessels in the eyes.
- Slowed pupillary light reflex as weed can reduce the speed and extent to which pupils constrict in response to bright light. This can make them look bigger in certain light conditions without having dilated at all.
- Droopy eyelids (ptosis) and an overall relaxed or tired appearance to the eye region of the face.
Marijuana can still cause visual impairments including mild hallucinations and slowed reaction times to visual stimulus.
What Are The Effects of Drugs on The Eyes?
 Psychotropic drugs can affect the eyes in multiple different ways. For example, psychotropic drugs can cause eyes to become dry or red. Psychotropic drugs can also cause people to experience blurry vision or rapid eye movement.
Psychotropic drugs can affect the eyes in multiple different ways. For example, psychotropic drugs can cause eyes to become dry or red. Psychotropic drugs can also cause people to experience blurry vision or rapid eye movement.
Dilated pupils are a product of the actions of the parasympathetic nervous system that aims to keep the body stable. As a result, certain prescription drugs such as SSRI antidepressants and heart medication have been known to cause dilated pupils.
Since the muscles in the eyes contract or expand, psychotropic drugs manipulate the normal function of the pupil, although such manipulation is rarely permanent. Although dilated pupils are a tell-tale sign of substance abuse, it’s important to check to see if there are other bodily signs of substance abuse such as one’s temperature, breathing, and heart rate prior to diagnosing an individual. This is particularly necessary for medical professionals when dealing with drug overdoses. Since psychotropic substances alter the parasympathetic nervous system, expect changes to happen in normal functioning.
The parasympathetic nervous system plays an important role in the overall guidance of the human body. For example. the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for making bodily duties occur such as one’s heart rate, pupil constriction, and digestion.
The parasympathetic activates when the body is in a relaxed state. The system is also critical for the production of urine, saliva, and mucus. Think of the parasympathetic nervous system as the company manager for these essential products.
What Does It Mean When Pupils Dilate?
Let’s say you’ve been feeling sick for the past couple of days and your body is sensitive. There you are, patiently sitting on the hospital bed. Your doctor asks you to cough, checks your blood pressure, and tops it off with a flashlight in your eyes. The light causes your pupils to shrink before going back to normal. Why is that happening?
The light passes through the cornea to the pupil before the iris controls the amount of light. Once it reaches the lens, the light becomes focused through the retina. Afterward, the information is registered to the back of the eye structure where it’s inverted. The optic nerve and visual cortex are responsible for interpreting and displaying the image for you to view.
A good visual metaphor for this is to imagine that your brain is a camera and your eyes are the lenses/sensors that take in a picture. Your lens can take in the light and transmits that information into the camera so you can see that breathtaking picture of the Rocky Mountains. The lens glass opens and closes to focus on what’s in front but if the glass is broken/dirty, then your picture is going to look out of touch.
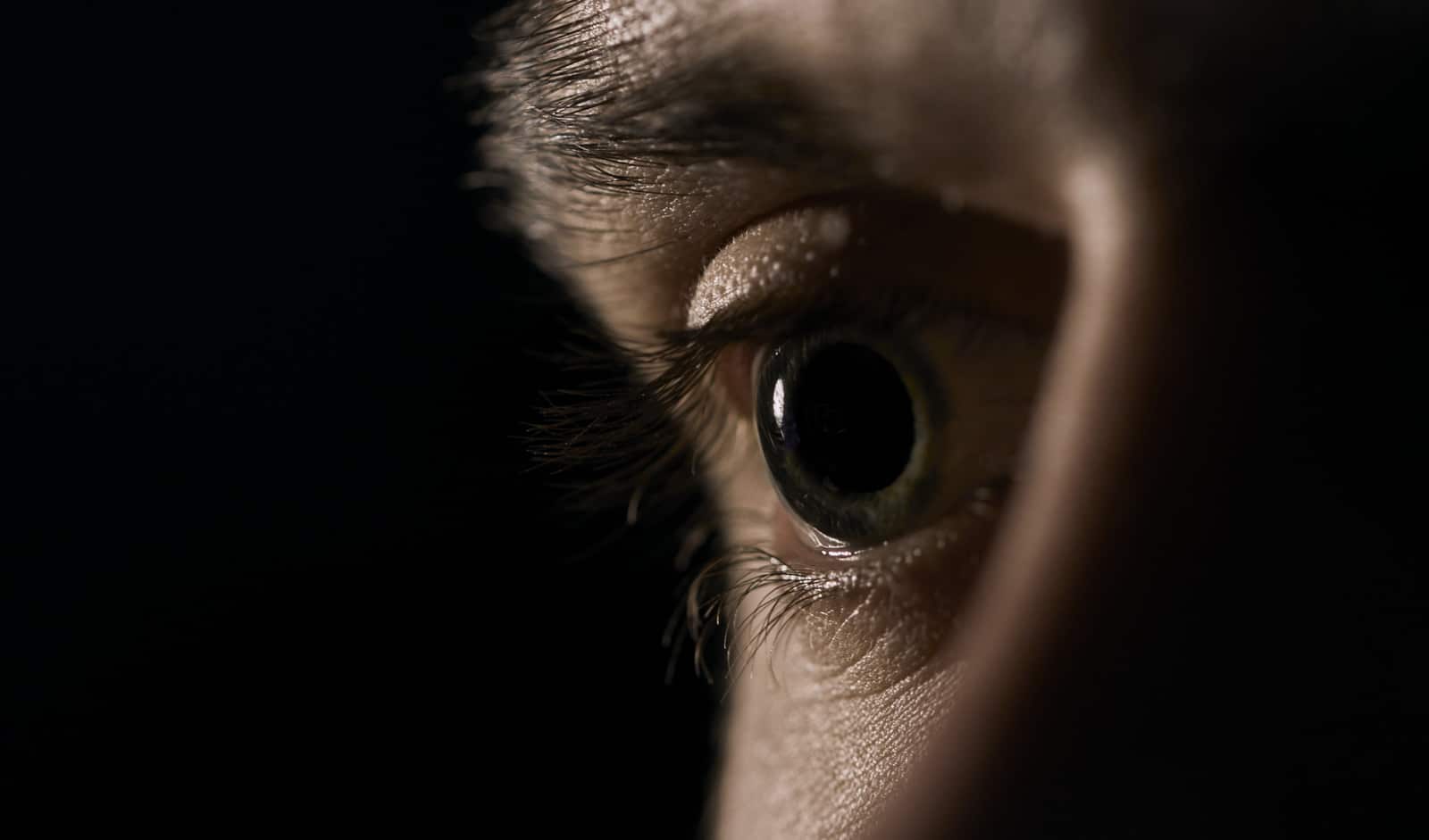

 Psychotropic drugs can affect the eyes in multiple different ways. For example, psychotropic drugs can cause eyes to become dry or red. Psychotropic drugs can also cause people to experience blurry vision or rapid eye movement.
Psychotropic drugs can affect the eyes in multiple different ways. For example, psychotropic drugs can cause eyes to become dry or red. Psychotropic drugs can also cause people to experience blurry vision or rapid eye movement.